In the rapidly evolving landscape of healthcare technology, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. As healthcare organizations increasingly rely on digital systems to manage patient data, streamline operations, and deliver care, the risks associated with cyber threats have grown exponentially. One of the most significant yet often overlooked challenges in this domain is technical debt.
Technical debt refers to the implied cost of additional rework caused by choosing an easy, limited, or quick solution now instead of using a better approach that would take longer. In the context of healthcare, technical debt can severely compromise cybersecurity and hinder effective incident response.
This article delves into the critical role of addressing technical debt in bolstering healthcare cybersecurity and incident response, supported by insights, facts, and figures.
The Growing Threat Landscape in Healthcare
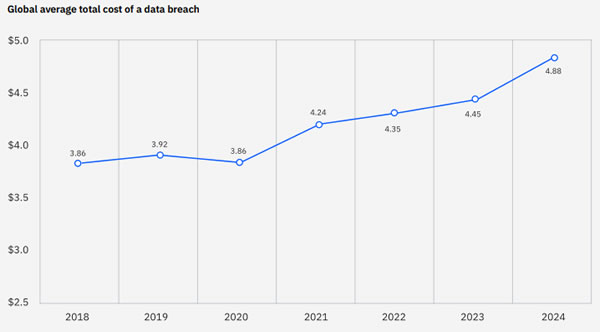
Healthcare has become one of the most targeted sectors for cyberattacks. According to a report by IBM, the healthcare industry experienced the highest average cost of a data breach in 2023, at $10.93 million per incident, up from $9.42 million in 2022 (IBM Security, 2023). The sensitive nature of patient data, coupled with the critical need for uninterrupted healthcare services, makes the sector a lucrative target for cybercriminals.
The COVID-19 pandemic further exacerbated the situation, as healthcare organizations rapidly adopted digital solutions to cope with the surge in demand for telehealth and remote patient monitoring.
This rapid digital transformation often led to the accumulation of technical debt, as organizations prioritized speed over security. A study by the Ponemon Institute found that 56% of healthcare organizations experienced a ransomware attack in 2022, with 67% of those attacks resulting in the encryption of data (Ponemon Institute, 2022).
Understanding Technical Debt in Healthcare
Technical debt in healthcare can manifest in various forms, including outdated software, unpatched systems, and poorly integrated technologies. These issues can create vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit.
For instance, the WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017, which affected the UK’s National Health Service (NHS), exploited vulnerabilities in outdated Windows operating systems. The attack disrupted healthcare services, canceled thousands of appointments, and caused significant financial losses.
A survey by the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) revealed that 70% of healthcare organizations still use legacy systems, many of which are no longer supported by vendors (HIMSS, 2021). These legacy systems often lack the necessary security features to defend against modern cyber threats, making them a prime target for attackers.
The Impact of Technical Debt on Cybersecurity
Technical debt can have a profound impact on an organization’s cybersecurity posture. Outdated systems and software are more susceptible to vulnerabilities, as they may not receive regular security updates or patches. This creates a fertile ground for cyberattacks, as attackers can exploit known vulnerabilities that have not been addressed.
Moreover, technical debt can hinder an organization’s ability to detect and respond to cyber incidents effectively. A report by the SANS Institute found that 60% of healthcare organizations lack the necessary tools and processes to detect and respond to cyber threats in real-time (SANS Institute, 2022). This is often due to the complexity and fragmentation of IT systems, which can make it difficult to monitor and secure the entire network.
The financial implications of technical debt are also significant. According to a study by Gartner, organizations that fail to address technical debt can incur costs that are up to 40% higher than those that proactively manage it (Gartner, 2024). These costs include not only the direct expenses associated with cyber incidents, such as ransom payments and regulatory fines, but also the indirect costs of reputational damage and lost patient trust.
The Role of Incident Response in Mitigating Cyber Risks
Effective incident response is critical for minimizing the impact of cyber incidents and ensuring the continuity of healthcare services. However, technical debt can severely impede an organization’s ability to respond to incidents promptly and effectively. For instance, outdated systems may not support the latest security tools and technologies, making it difficult to detect and contain threats.
A well-defined incident response plan is essential for mitigating the risks associated with technical debt. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), an effective incident response plan should include the following key components: preparation, detection and analysis, containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident activities (NIST, 2012). However, many healthcare organizations struggle to implement these components due to the limitations imposed by technical debt.
The importance of incident response is underscored by the fact that the average time to identify and contain a data breach in healthcare is 287 days, compared to 277 days across all industries (IBM Security, 2023). This extended timeframe can result in more extensive damage and higher costs, highlighting the need for healthcare organizations to invest in robust incident response capabilities.
Strategies for Addressing Technical Debt
Addressing technical debt requires a proactive and strategic approach. Healthcare organizations must prioritize cybersecurity and allocate the necessary resources to modernize their IT infrastructure. The following strategies can help organizations reduce technical debt and enhance their cybersecurity posture:
- Conduct a Comprehensive Assessment: The first step in addressing technical debt is to conduct a thorough assessment of the organization’s IT infrastructure. This includes identifying outdated systems, unpatched software, and poorly integrated technologies. The assessment should also evaluate the organization’s cybersecurity policies and procedures to identify areas for improvement.
- Develop a Modernization Plan: Based on the assessment, organizations should develop a comprehensive modernization plan that outlines the steps needed to address technical debt. This plan should prioritize critical systems and applications that are most vulnerable to cyber threats. It should also include a timeline for implementing security updates and patches.
- Invest in Cybersecurity Training: Human error is one of the leading causes of cyber incidents in healthcare. Investing in cybersecurity training for staff can help reduce the risk of incidents caused by phishing attacks, weak passwords, and other common vulnerabilities.
- Implement Advanced Security Technologies: Healthcare organizations should invest in advanced security technologies, such as intrusion detection systems, endpoint protection, and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions. These technologies can help detect and respond to cyber threats in real-time, reducing the impact of incidents.
- Establish a Robust Incident Response Plan: A well-defined incident response plan is essential for minimizing the impact of cyber incidents. The plan should include clear roles and responsibilities, as well as procedures for detecting, containing, and recovering from incidents. Regular testing and updating of the plan are also critical to ensure its effectiveness.
- Collaborate with Industry Partners: Healthcare organizations should collaborate with industry partners, including vendors, regulators, and other stakeholders, to share best practices and stay informed about emerging threats. Participating in information-sharing initiatives, such as the Health Information Sharing and Analysis Center (H-ISAC), can help organizations stay ahead of cyber threats.
The Benefits of Addressing Technical Debt
Addressing technical debt can yield significant benefits for healthcare organizations, including improved cybersecurity, enhanced patient care, and reduced costs. By modernizing their IT infrastructure and implementing robust security measures, organizations can reduce the risk of cyber incidents and ensure the continuity of healthcare services.
Moreover, addressing technical debt can help organizations comply with regulatory requirements, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Compliance with these regulations is essential for avoiding costly fines and maintaining patient trust.
In addition, reducing technical debt can improve operational efficiency and enable healthcare organizations to leverage emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), to enhance patient care. For instance, AI-powered diagnostic tools can help clinicians make more accurate and timely diagnoses, while ML algorithms can analyze large datasets to identify trends and improve treatment outcomes.
In Conclusion
Technical debt is a critical issue that healthcare organizations must address to enhance their cybersecurity and incident response capabilities. The growing threat landscape, coupled with the increasing reliance on digital systems, makes it imperative for organizations to prioritize the modernization of their IT infrastructure. By conducting comprehensive assessments, developing modernization plans, investing in cybersecurity training, and implementing advanced security technologies, healthcare organizations can reduce technical debt and mitigate the risks associated with cyber threats.
The benefits of addressing technical debt extend beyond cybersecurity, encompassing improved patient care, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, organizations that proactively manage technical debt will be better positioned to navigate the challenges of the digital age and deliver high-quality care to their patients.
 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 简体中文
简体中文