The financial services industry, particularly retail banking, faces an ever-evolving landscape of fraud and credit risk, and the cost for these fields keeps rising, according to McKinsey. As cybercriminals deploy more sophisticated tactics and global economies experience greater volatility, banks must harness cutting-edge tools to safeguard their operations and customers. Digitalization and generative AI (AI) have emerged as transformative solutions, enabling banks to detect fraud and manage credit risk with unprecedented speed, accuracy, and efficiency. Below, we explore three key ways these technologies empower retail banks to stay ahead of threats.
1. Real-Time Fraud Detection and Prevention
Fraud remains one of the most significant challenges for retail banks, with global financial losses from cybercrime expected to exceed $10 trillion annually by 2025. Digitalization and AI have revolutionized fraud detection by enabling real-time monitoring and intervention. Here’s how:
a. Advanced Behavioral Analytics
Traditional fraud detection systems rely on static rule-based mechanisms that often miss subtle anomalies in customer behavior. Digitalized platforms augmented by AI can analyze vast datasets in real-time to identify patterns indicative of fraudulent activity. For example:
- Monitoring transactional data to detect unusual activity, such as sudden large withdrawals or transfers to unfamiliar accounts.
- Cross-referencing geolocation data with spending habits to flag transactions made from improbable locations.
JPMorgan Chase has implemented AI-driven systems to enhance its fraud detection capabilities. This has led to reduced fraud levels and an improved customer experience, with account validation rejection rates decreasing by 15-20%.
b. Generative AI for Synthetic Fraud Models
AI plays a unique role in combating fraud by creating synthetic datasets that mimic fraudulent behaviors. These models help banks:
- Train machine learning algorithms to recognize emerging fraud tactics.
- Simulate attacks to stress-test fraud detection systems, ensuring readiness against sophisticated threats.
Swedbank utilized Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to detect fraudulent transactions. GANs are trained to learn legal and illegal transactions to identify fraudulent activities effectively.
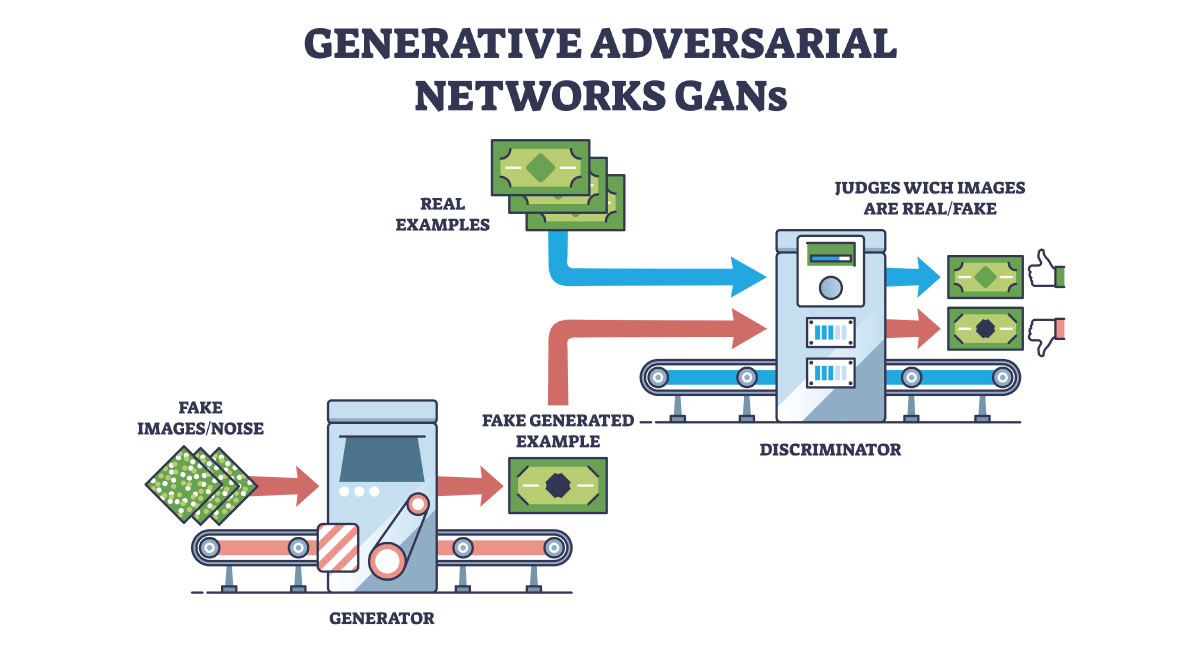
c. Intelligent Automation
Digitalization enables seamless integration of AI-powered fraud prevention tools into banking ecosystems. Automated systems can:
- Freeze suspicious transactions in real-time while alerting both the bank and the customer.
- Escalate high-risk cases to fraud analysts for manual review, reducing false positives and enhancing customer trust.
Commonwealth Bank of Australia (CBA) has significantly invested in AI technologies to enhance its fraud prevention mechanisms. The bank reported a 50% reduction in scam losses after implementing AI-driven systems that monitor and act upon suspicious activities in real-time.
2. Enhanced Credit Risk Assessment
Assessing credit risk is a core function of retail banks, yet traditional methods often rely on outdated data and static scoring models. Digitalization and AI empower banks to adopt more nuanced, dynamic approaches, improving their ability to evaluate creditworthiness accurately.
a. Comprehensive Data Integration
Digitalized systems aggregate data from diverse sources, including:
- Traditional financial metrics like income, credit history, and outstanding debt.
- Non-traditional data, such as utility payments, rental history, and even social media behavior. This holistic view allows banks to assess risk more accurately, especially for individuals with limited credit history (“thin file” customers).
b. Real-Time Risk Monitoring
With digital platforms, banks can move beyond point-in-time credit assessments to continuous monitoring. AI models analyze real-time data streams to:
- Detect early warning signs, such as declining account balances or missed payments.
- Adjust risk profiles dynamically, enabling banks to take preemptive actions, such as offering refinancing options to at-risk borrowers.
c. Predictive Analytics for Credit Decisions
AI’s ability to identify patterns and predict outcomes is a game-changer for credit risk management. Key applications include:
- Developing predictive models that estimate the likelihood of default for specific customer segments.
- Offering personalized loan terms based on real-time risk assessments, optimizing profitability while minimizing exposure.
3. Regulatory Compliance and Risk Mitigation
The financial industry is heavily regulated, with strict requirements to prevent money laundering, financing of terrorism, and other illicit activities. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and reputational damage. Digitalization and AI streamline compliance processes while enhancing overall risk management.
Mastercard plans to acquire cybersecurity firm Recorded Future for $2.65 billion, enhancing its fraud prevention and cybersecurity services with Recorded Future’s technology, including AI. This acquisition underscores the rising importance of threat intelligence amid escalating cyber threats from criminal and nation-state actors
a. Automated Regulatory Reporting
Digitalization eliminates the manual, error-prone processes traditionally associated with regulatory reporting. AI-driven platforms can:
- Aggregate and analyze transaction data to identify suspicious activities.
- Generate accurate, comprehensive reports for regulators, reducing the burden on compliance teams.
b. Generative AI for Document Analysis
Retail banks deal with vast amounts of unstructured data, such as customer communications and loan agreements. AI tools can:
- Extract, summarize, and analyze information from documents to identify compliance risks.
- Highlight inconsistencies or gaps in documentation, enabling proactive remediation.
c. Risk Scenario Simulation
AI allows banks to simulate various risk scenarios, helping them prepare for potential regulatory or operational challenges. For instance:
- Stress-testing portfolios under different economic conditions to assess resilience.
- Modeling the impact of new regulations on existing compliance frameworks.
The Future of Fraud and Risk Management in Retail Banking
As the financial services industry continues to digitalize, the role of AI will only grow more pivotal. Banks that invest in these technologies today will be better equipped to combat fraud, manage credit risk, and navigate an increasingly complex regulatory landscape. The benefits extend beyond risk mitigation: enhanced customer trust, streamlined operations, and new opportunities for growth.
However, the adoption of digitalization and AI is not without challenges. Data privacy, ethical considerations, and the need for robust cybersecurity measures must remain top priorities. Retail banks must strike a balance between leveraging technology and safeguarding customer rights.
In conclusion, the combination of digitalization and generative AI offers retail banks a powerful arsenal to address fraud and credit risk. By staying at the forefront of technological innovation, banks can not only protect their operations but also unlock new avenues for growth and customer satisfaction. The future of retail banking is digital, and the time to act is now.
 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 简体中文
简体中文