As of January 14, 2025, the U.S. government has implemented a landmark regulation banning the sale and import of Chinese and Russian technology in passenger vehicles. This decisive move, driven by national security concerns, presents both significant challenges and opportunities for software development managers and technical leads in the automotive industry. For those navigating this evolving regulatory landscape, understanding the implications and preparing actionable strategies will be critical for maintaining compliance and competitiveness.
Overview of the Ban
The U.S. Department of Commerce has outlined stringent rules targeting connected vehicle hardware and software systems originating from Chinese and Russian entities. These regulations, effective for upcoming model years, aim to protect sensitive automotive ecosystems from potential security vulnerabilities. Key elements of the ban include:
- Software Restrictions: Starting with the 2027 model year, any software tied to Chinese or Russian developers, companies, or subsidiaries is prohibited.
- Hardware Restrictions: Beginning with the 2030 model year, hardware components—including Vehicle Connectivity Systems (VCS) and Automated Driving Systems (ADS)—with links to these nations will also be banned.
- Scope: The ban applies universally to all passenger vehicles weighing less than 10,001 pounds, irrespective of the manufacturing location, if banned technologies are embedded.
This sweeping regulation demands an immediate and strategic response from automotive companies to mitigate risks, ensure compliance, and seize emerging opportunities in the evolving marketplace.
Implications for Software Development Managers
1. Compliance Challenges
The ban introduces significant complexities in ensuring that all software solutions meet U.S. regulatory standards. Software development managers must take proactive measures to avoid costly penalties and disruptions:
- Auditing Existing Software: Conduct comprehensive audits to identify any dependencies on Chinese or Russian software components. Tools such as Software Bill of Materials (SBOMs) can be employed to trace dependencies, libraries, and modules.
- Developing Alternative Solutions: Investments in R&D will be essential to replace non-compliant components with domestic or allied alternatives. Open-source platforms and partnerships with local startups can accelerate the development of compliant solutions.
- Compliance Training: Educate engineering and procurement teams on regulatory requirements to embed compliance considerations at every stage of development and sourcing.
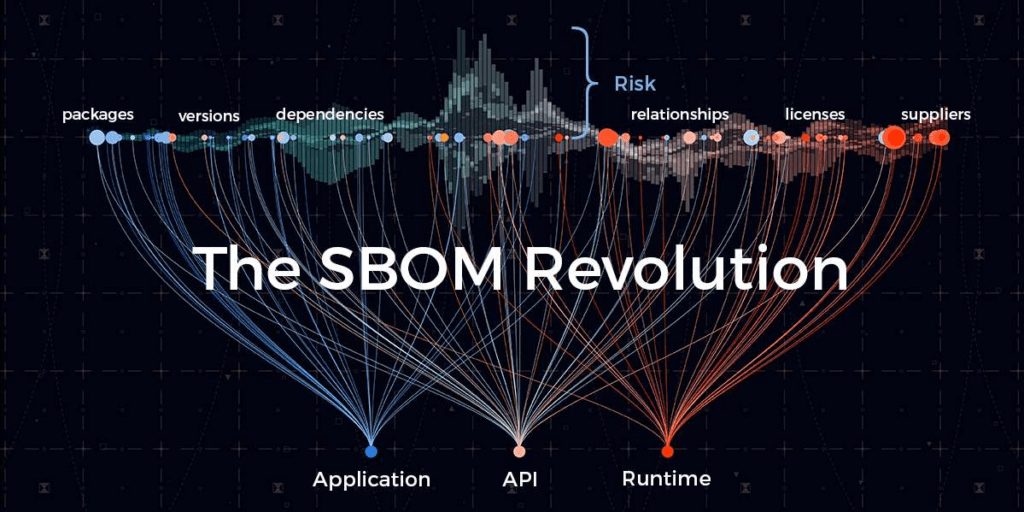
2. Increased Demand for Local and International Solutions
With manufacturers pivoting away from Chinese and Russian technology, there is a growing demand for solutions from countries not affected by the ban, such as Vietnam, Poland, and others. This shift highlights several strategic priorities:
- Partnership Opportunities: Collaborate with local or allied software vendors, including emerging tech hubs in regions like Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe, to co-develop solutions that align with U.S. regulations. Building such partnerships can also enhance innovation capacity and diversify expertise.
- Focus on Innovation: The demand for cutting-edge solutions—from advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) to seamless infotainment integration—creates fertile ground for innovation. Emphasizing cybersecurity, data privacy, and reliable over-the-air (OTA) updates can differentiate your solutions in a competitive landscape.
- Incentives for Local and International Development: State and federal incentives for domestic innovation, as well as international collaborations with compliant regions, such as grants or tax benefits, can reduce development costs and drive faster adoption of alternative technologies.
3. Strategic Sourcing Adjustments
The ban necessitates a fundamental reassessment of sourcing strategies, requiring a shift toward more secure and diversified supply chains:
- Supplier Vetting: Establish stringent vetting protocols to verify that third-party suppliers comply with U.S. regulations. Supplier audits, contractual obligations, and certifications (e.g., ISO/SAE 21434 for automotive cybersecurity) should become standard practice.
- Diversification of Suppliers: Reduce dependency on single suppliers by exploring partnerships with companies from compliant regions, including Europe, Japan, South Korea, India, and Vietnam. Diversification ensures supply chain resilience and reduces exposure to geopolitical risks.
- Adoption of Modular Architectures: Modular software architectures—such as service-oriented architecture (SOA)—enable easier replacement of individual non-compliant components without overhauling entire systems. This adaptability can simplify future updates and compliance efforts.

4. Future-Proofing Technology Investments
To stay competitive in this rapidly changing environment, investing in future-ready technologies will be critical. Key focus areas include:
- Cybersecurity Enhancements: With connected vehicles becoming prime targets for cyber threats, robust cybersecurity measures are essential. Techniques such as intrusion detection systems (IDS), end-to-end encryption, and secure boot processes should be prioritized.
- Alignment with Emerging Trends: The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving technologies presents an opportunity to integrate compliant software solutions into cutting-edge platforms. For example, leveraging AI-driven decision-making for ADAS can help manufacturers differentiate their offerings.
- Interoperability Standards: Adopting standards such as AUTOSAR (Automotive Open System Architecture) fosters compatibility and scalability while adhering to regulatory requirements.
- Testing and Certification: Preemptively pursuing certifications for new technologies ensures smooth regulatory approvals and builds trust with OEMs and consumers.
Opportunities for Growth and Innovation
While the U.S. ban imposes stringent requirements, it also creates avenues for growth and innovation. Companies willing to adapt can capitalize on these opportunities:
- Development of Secure Data Ecosystems: The ban underscores the importance of secure data handling in connected vehicles. Companies that invest in data protection technologies—such as blockchain for secure transactions or AI-driven anomaly detection—will be better positioned to lead the market.
- Localized Manufacturing and Development: Regional hubs for software and hardware development will gain prominence as manufacturers seek proximity to compliant suppliers. Establishing partnerships with universities and research institutions can further bolster regional innovation.
- Customer Trust: By emphasizing compliance and security, automotive companies can build greater trust with consumers. Transparency in sourcing and cybersecurity efforts can become a competitive differentiator in an increasingly connected and data-driven industry.
In Conclusion
The U.S. ban on Chinese and Russian technology in passenger vehicles marks a pivotal moment for the automotive industry. While the regulation presents undeniable challenges, it also provides a unique opportunity to innovate, localize, and lead in a secure automotive future.
For software development managers and tech leads, the path forward requires a multi-faceted approach: audit and replace non-compliant components, invest in local partnerships, diversify supply chains, and future-proof technologies. By staying informed and agile, companies can not only navigate this regulatory shift but also emerge stronger and more competitive in the global market.
As the automotive landscape continues to evolve, those who embrace compliance as a catalyst for innovation will drive the industry forward into a safer, more secure, and sustainable future.
 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 简体中文
简体中文